FSx for NetApp ONTAP CSI Driver
Before diving into this section, you should be familiar with the Kubernetes storage objects (volumes, persistent volumes (PV), persistent volume claims (PVC), dynamic provisioning and ephemeral storage) that were introduced in the main Storage section.
The Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP Container Storage Interface (CSI) Driver enables you to run stateful containerized applications by providing a CSI interface that allows Kubernetes clusters running on AWS to manage the lifecycle of Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP file systems.
The following architecture diagram illustrates how we will use FSx for NetApp ONTAP as persistent storage for our EKS pods:
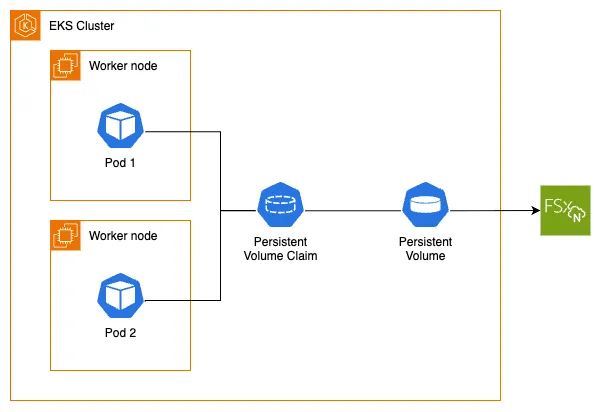
To utilize Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP with dynamic provisioning on our EKS cluster, we first need to confirm that we have the FSx for NetApp ONTAP CSI Driver installed. The driver implements the CSI specification which allows container orchestrators to manage Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP file systems throughout their lifecycle.
We can install the Amazon FSxN for NetApp ONTAP Trident CSI driver using helm. We will need to provide a required IAM role that has already been created for us as part fo the preparation for the workshop.
We can confirm the installation like so:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
trident-controller-b6b5899-kqdjh 6/6 Running 0 87s
trident-node-linux-9q4sj 2/2 Running 0 86s
trident-node-linux-bxg5s 2/2 Running 0 86s
trident-node-linux-z92x2 2/2 Running 0 86s
trident-operator-588c7c854d-t4c4x 1/1 Running 0 102s
An FSx for NetApp ONTAP file system has been provisioned for us, along with the Storage Virtual Machine (SVM) and the required security group that includes an inbound rule allowing NFS traffic to the FSx mount points. Let's get its ID which we'll need later:
fs-0123456789abcdef0
The FSx for NetApp ONTAP CSI driver supports both dynamic and static provisioning:
- Dynamic provisioning: The driver creates volumes on the existing FSx for NetApp ONTAP file system. This requires an existing AWS FSx for NetApp ONTAP file system that must be specified in the StorageClass parameters.
- Static provisioning: This also requires a pre-created AWS FSx for NetApp ONTAP file system, which can then be mounted as a volume inside a container using the driver.
Next, we'll create a TridentBackendConfig object configured to use the pre-provisioned FSx for NetApp ONTAP file system. For this, lets examine the fsxn-backend-nas.yaml file we'll be using to create the backend:
apiVersion: trident.netapp.io/v1
kind: TridentBackendConfig
metadata:
name: backend-tbc-ontap-nas
namespace: trident
spec:
version: 1
storageDriverName: ontap-nas
backendName: tbc-ontap-nas
svm: ${EKS_CLUSTER_NAME}-svm
aws:
fsxFilesystemID: ${FSXN_ID}
credentials:
name: "${FSXN_SECRET_ARN}"
type: awsarn
Inject EKS_CLUSTER_NAME environment variable into the svm parameter - This is the Storage Virtual Machine name
Inject FSXN_ID environment variable into the fsxFilesystemID parameter - This is the FSxN filesystem we're going to connect our CSI driver to
Inject FSXN_SECRET_ARN environment variable into the credentials.name parameter - This is the ARN of a secret stored securely in AWS Secrets Manager, which contains the credentials to connect to the ONTAP API interface
Apply the backend configuration:
tridentbackendconfig.trident.netapp.io/backend-tbc-ontap-nas created
Verify that the TridentBackendConfig was created:
NAME BACKEND NAME BACKEND UUID PHASE STATUS
backend-tbc-ontap-nas tbc-ontap-nas bbae8686-25e4-4fca-a4c7-7ab664c7db9c Bound Success
Now let's create the StorageClass object using the fsxnstorageclass.yaml file:
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: fsxn-sc-nfs
provisioner: csi.trident.netapp.io
parameters:
backendType: "ontap-nas"
allowVolumeExpansion: True
Set the provisioner parameter to csi.trident.netapp.io for the Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP CSI provisioner
Set the backendType to ontap-nas to indicate that the ONTAP NAS driver should be used for accessing the ONTAP volume
Apply the StorageClass:
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/fsxn-sc-nfs created
Let's examine the StorageClass. Note that it uses the FSx for NetApp ONTAP CSI driver as the provisioner and is configured for ONTAP NAS provisioning mode:
NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE
fsxn-sc-nfs csi.trident.netapp.io Delete Immediate true 8m29s
Name: fsxn-sc-nfs
IsDefaultClass: No
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration={"allowVolumeExpansion":true,"apiVersion":"storage.k8s.io/v1","kind":"StorageClass","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"fsxn-sc-nfs"},"parameters":{"backendType":"ontap-nas"},"provisioner":"csi.trident.netapp.io"}Provisioner: csi.trident.netapp.io
Parameters: backendType=ontap-nas
AllowVolumeExpansion: True
MountOptions: <none>
ReclaimPolicy: Delete
VolumeBindingMode: Immediate
Events: <none>
Now that we understand the FSx for NetApp ONTAP StorageClass and how the FSx for NetApp ONTAP CSI driver works, we're ready to proceed to the next step where we'll modify the UI component to use the FSx for NetApp ONTAP StorageClass with Kubernetes dynamic volume provisioning and a PersistentVolume for storing product images.