Deploying an application
Now that we have successfully configured Argo CD on our cluster, let's deploy an application. To demonstrate the difference between a GitOps-based delivery approach and traditional deployment methods, we'll migrate the UI component of our sample application from using the kubectl apply -k approach to an Argo CD-managed deployment.
An Argo CD application is a Custom Resource Definition (CRD) that represents a deployed application instance in an environment. It defines key information such as the application name, Git repository location, and path to the Kubernetes manifests. The application resource also specifies the desired state, target revision, sync policy, and health check policy.
First, let's remove the existing sample application from the cluster:
namespace "carts" deleted
namespace "catalog" deleted
namespace "checkout" deleted
namespace "orders" deleted
namespace "other" deleted
namespace "ui" deleted
Now we'll populate our Git repository with a simple Helm chart which wraps the published chart for the UI component by using it as a Helm dependency:
apiVersion: v2
name: retail-store-sample-chart
description: A Helm chart for the AWS retail store ui component
type: application
version: 0.0.1
dependencies:
- name: retail-store-sample-ui-chart
alias: ui
version: 1.2.1
repository: oci://public.ecr.aws/aws-containers
The name of the wrapper Helm chart
Indicates this chart deploys an application
Specify a version for the chart
Specify the name, alias and version of the retail store UI component from AWS's public OCI registry as the dependency of the wrapper Helm chart
Let's copy this file to our Git directory:
Our Git directory should now have this structure:
`-- ui
`-- Chart.yaml
Now we'll push our configuration to the Git repository:
Next, let's create an Argo CD Application configured to use our Git repository:
application 'ui' created
We can verify that the application has been created:
NAME CLUSTER NAMESPACE PROJECT STATUS HEALTH SYNCPOLICY CONDITIONS
argocd/ui https://kubernetes.default.svc ui default OutOfSync Missing Manual <none>
This application is now visible in the Argo CD UI:
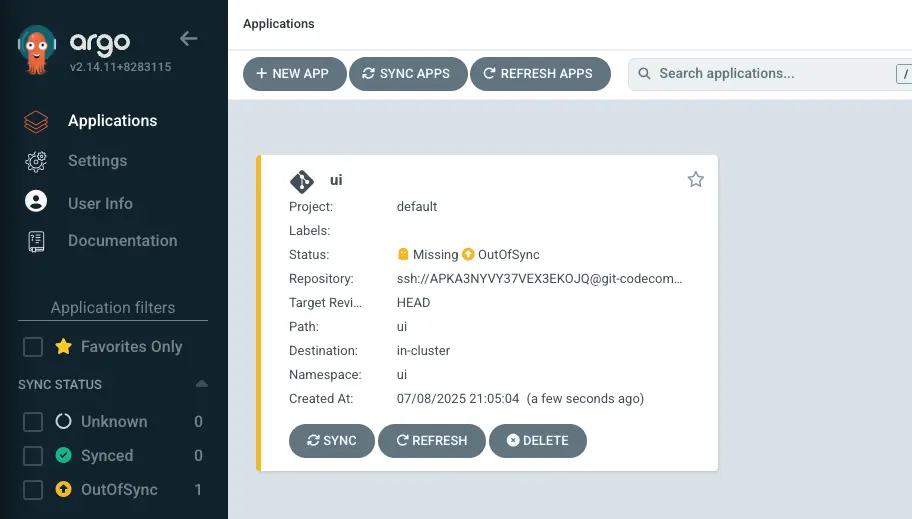
Alternatively, we can also interact with Argo CD objects directly using the kubectl command:
NAME SYNC STATUS HEALTH STATUS
apps OutOfSync Missing
If you open the Argo CD UI and navigate to the apps application, you'll see:
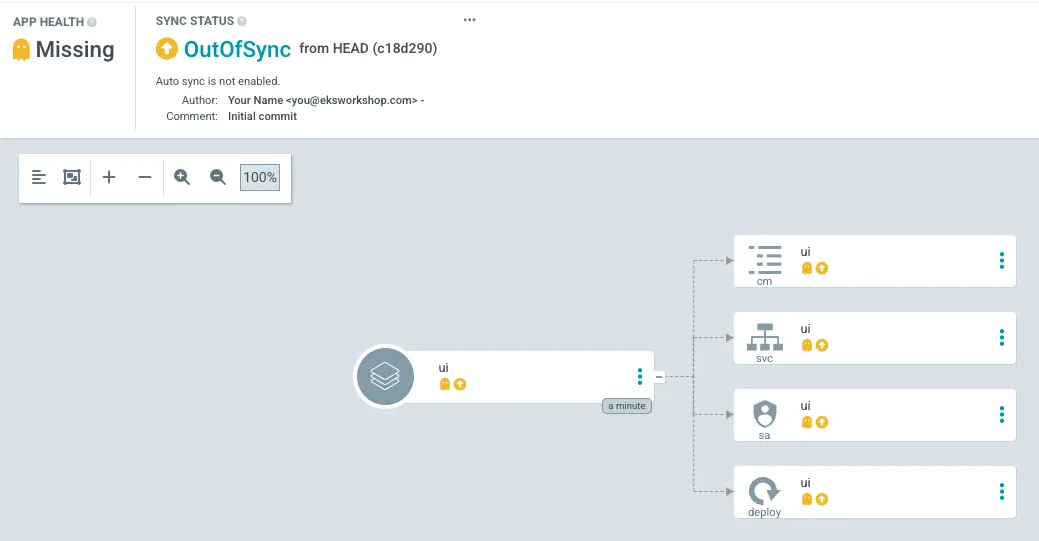
In Argo CD, "out of sync" indicates that the desired state defined in your Git repository doesn't match the actual state in your Kubernetes cluster. Although Argo CD is capable of automated synchronization, for now we'll manually trigger this process:
After a short period, the application should reach the Synced state, with all resources deployed. The UI should look like this:
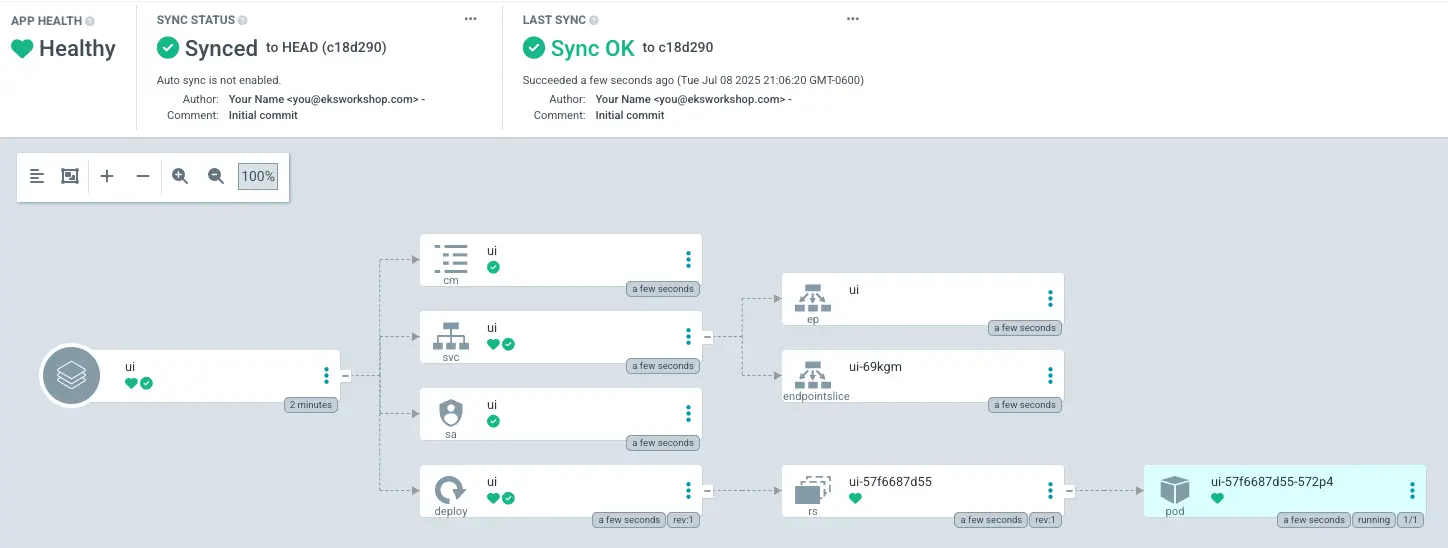
This confirms that Argo CD has successfully installed the Helm chart and it's now in sync with the cluster.
We've now successfully migrated the UI component to be deployed using Argo CD. Any future changes pushed to the Git repository will be automatically reconciled to our EKS cluster.
To verify that all resources related to the UI service are deployed, run the following commands:
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
ui 1/1 1 1 61s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
ui-6d5bb7b95-rjfxd 1/1 Running 0 62s