Updating an application
Now that we have deployed our application with Argo CD, let's explore how we can use GitOps principles to update its configuration. In this example, we'll increase the number of replicas for the ui deployment from 1 to 3 using Helm values.
First, we'll create a values.yaml file that configures the number of replicas:
ui:
replicaCount: 3
Let's copy this configuration file to our Git repository directory:
After adding this file, our Git directory structure should look like this:
`-- ui
|-- Chart.yaml
`-- values.yaml
Now we'll commit and push our changes to the Git repository:
At this point, Argo CD will detect that the application state in the repository has changed. You can either click Refresh and then Sync in the Argo CD UI, or use the argocd CLI to synchronize the application:
After synchronization completes, the UI deployment should now have 3 pods running:
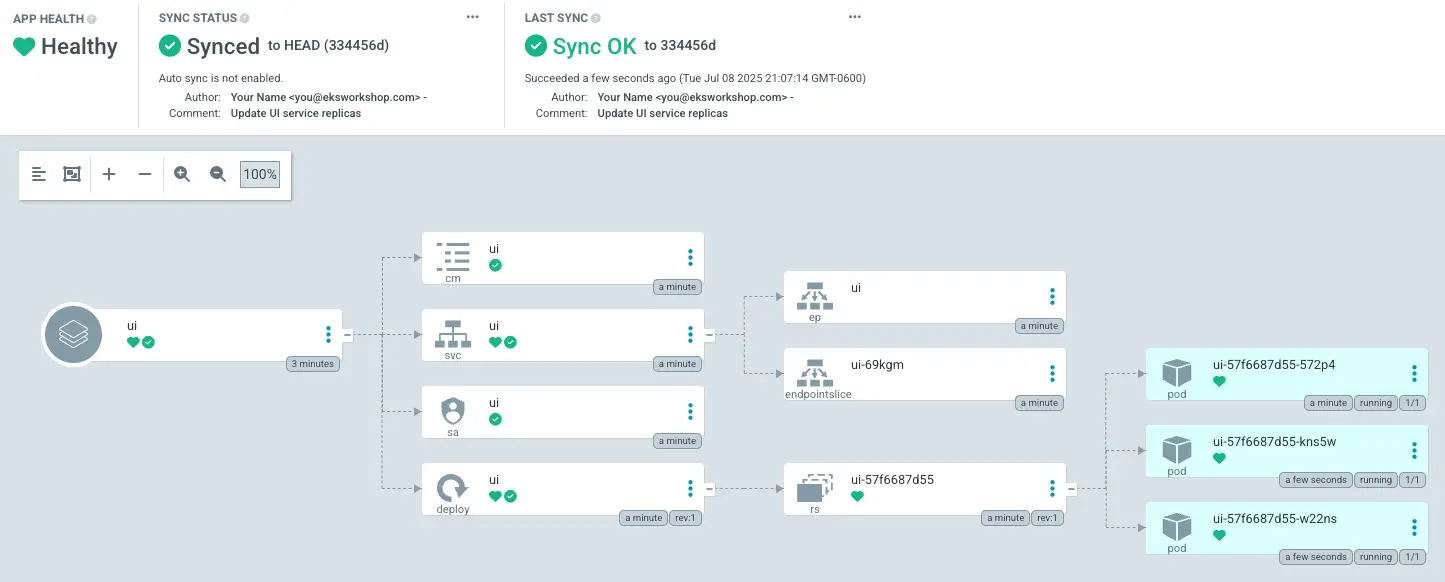
To verify that our update was successful, let's check the deployment and pod status:
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
ui 3/3 3 3 3m33s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
ui-6d5bb7b95-hzmgp 1/1 Running 0 61s
ui-6d5bb7b95-j28ww 1/1 Running 0 61s
ui-6d5bb7b95-rjfxd 1/1 Running 0 3m34s
This demonstrates how GitOps allows us to make configuration changes through version control. By updating our repository and syncing with Argo CD, we've successfully scaled our UI deployment without directly interacting with the Kubernetes API.